"MITM Attack"👿
💥After the post on the Phishing Attack(link here 👀), let us move towards a hacking attack which requires three players(You can see diagram below), this attack is called the "Man In The Middle" Attack.
So let us get started...

👉Introduction:
As you can see in the diagram above, there are three players in the MITM Attack the victim, the destination where the victim is trying to connect/communicate, and the man-in-the-middle who is intercept between these two.
MITM Attacks come in the two forms one involves physical presence around the target and the other involves malware.
Cybercriminals typically execute this attack in two phases:
‣ Interception
‣ Decryption
In a classical MITM Attack, the cybercriminal gains access to the unprotected Wi-Fi hotspots in public areas or homes. Attackers scan the other connected devices, check vulnerabilities such as a weak password.
Once the attacker found a vulnerability, attacks the target and read its data as an intercept. Attackers can also deploy tools to get banking as well as personal information.
👉How it works?:
Let's say you have received an email looking like it is from your bank, you click on the link provided in it and directed towards a page similar to your bank's login and perform the task mentioned.
In such a scenario, the man in the middle(MITM) has sent you the email, making it appear legitimate(this involves phishing). He also created a website that looks like your bank's website. But while you are performing the log in the task, you are handing over your credentials to the attacker.
This attack is called the man in the browser(MITB) attack.
👉Types of MITM Attacks:
1. IP Spoofing:
As per our homes, each device connecting to the internet has its address named as IP(Internet Protocol). By IP spoofing, an attacker can trick you like you're interacting with a website or internet entity you are not but giving the attacker access to information(and you know nothing😃!!)
2. DNS Spoofing:
The following picture can show you all about what a DNS Spoofing Attack is...
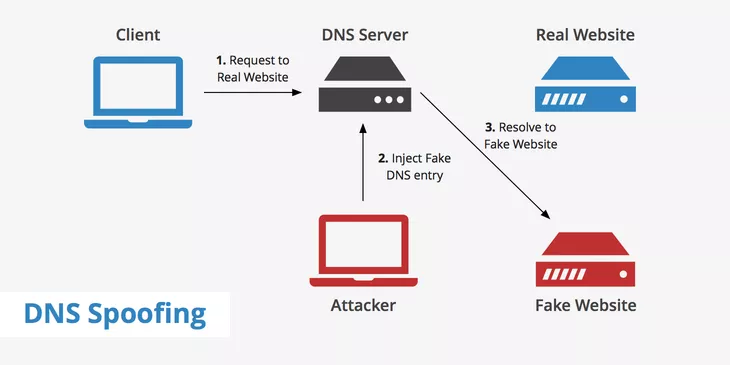
DNS(Domain Name System) Spoofing ts a technique by which an attacker can force a user to interact with a website that looks like it is the original one but actually it is a fraudster. The attacker's goal is to divert traffic from the real site or capture the login credentials.
3. HTTPS Spoofing:
In HTTPS, 'S' stands for security. It is the sign that the website is secure to interact with. Attackers can fool you and your browser believing it is secure and can spy you and keep a track of your personal information.
4. SSL Hijacking:
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, a protocol that establishes encrypted links between your browser and the webserver. In SSL Hijacking, a hacker uses another computer with a secure connection to become an intercept between the user's server and computer for information passing.
5. Email Hijacking:
In this, the cybercriminals target banks and other financial institutions. After gaining access, they can monitor customer transactions. Then they spoof bank email and send fake emails to the customers as real ones. The process ends up by putting the customer's own money in the attacker's hands.
6. Stealing Browser Cookies:
A cookie is a small piece of information a website stores on your computer. Cookie stores important credentials so that you don't have to re-enter them again and again. Since cookies store your important information, a cybercriminal can gain access to your sensitive information.
👉How to Detect and Prevent MITM Attack:
Actually, detecting a MITM Attack is not an easy task. Many of the MITM Attacks have fulfilled their intends before the user gets known to them. But MITM Attack can be prevented when someone takes proper steps towards authentication of servers he/she browses or interacts with and keeping them updated.
Here are some best practices to prevent from MITM Attack and getting safe:
• Having a strong encryption on your wireless networks will always help you to get rid of other users from interfering.
• Keep your Wi-Fi and router connection passwords strong.
• Use VPNs(Virtual Private Networks) to set up your own network
zone. They use key-based encryption for a secure connection.
• Users can use browser plug-ins to enforce using HTTPS over HTTP.
• Make sure that the DNS servers that you use are secure. by
checking the configuration on your router.
See you in the next post guys...Stay secure...😊😊
Comments
Post a Comment