"Packet Sniffing"
Hello Friends...😃
In the last few posts we are going through each hacking attack like MITM(link here👀), Brute Force, Phishing, SQL injection thoroughly, and discussing the preventive measures to prevent such cyber attacks. But these were the attacks we were doing on a remote system or computer. Let us move towards the hacking attacks that are done on wireless networks...
👉Introduction:
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between two or more devices connected to it or within each other. Wireless meaning that these networks are connected via cables of any kind. Wireless techniques allow users to avoid the costly process of having wires over the buildings, tower stations, elimination of energy due to attenuation as a connection between two locations.
A wireless router is a hardware device that internet providers use to connect users with the internet. A router can connect a local network to other local networks or the internet. Most attackers use network sniffing to find the SSID and hack a wireless network.
Sniffing is the process of monitoring and capturing all the data packets passing through a given network using sniffing tools. The best example of sniffing can be "tapping" of phone numbers. Sniffing allows us to sort all types of traffic: Private and Protected. Any information between two networks can be analyzed by intercepting the data packets.
Sniffers are the software or hardware programs that are used to extract or steal the information that is transmitted over the network.
👉How it works?:
A sniffer normally turns the NICs(Network Interface Cards) of the system to the promiscuous mode so that it listens to all the data transmitted on its segment. Promiscuous mode refers to a unique way of Ethernet hardware, in particular, NICs, that allows a NIC to receive all the traffic on the network, even if it is not addressed to this NIC. By default, NIC ignores all the traffic that is not addressed to it which is done by comparing the destination address of the Ethernet packet with the hardware address, that is, the MAC address of the device.

While this makes perfect sense for networking, non-promiscuous mode makes it difficult to use network monitoring and analysis software for diagnosing connectivity issues or traffic accounting.
The motives of attackers behind the sniffing attack can be: getting usernames and passwords, stealing bank transaction-related information, identity theft, email spying.
👉Types of Sniffing:
• Active Sniffing:
Access points are the network data logical switches. Switches use the Media Access Control(MAC) address to forward information to their intended destination ports. Active sniffing is used to sniff a switch-based network. It involves injecting Address Resolution Packets(ARP) into a target network to flood on the switch Content Addressable Memory(CAM) table. CAM keeps a track of which port is connected to which port. The attacker has to inject network traffic into the LAN to enable sniffing of the traffic. Refer to the diagram below.
• Passive Sniffing:
Passive Sniffing uses hubs instead of switches. Hubs perform the
same way as switches only that they do use MAC addresses to read the
destination ports of data. All an attacker needs to do is simply connect to LAN
and they can sniff data traffic in that network. Since hub networking is not
used today, passive sniffing is not used to perform the attack nowadays. Refer the figure below:
👉Top Sniffing Tools:
‣ Wireshark:
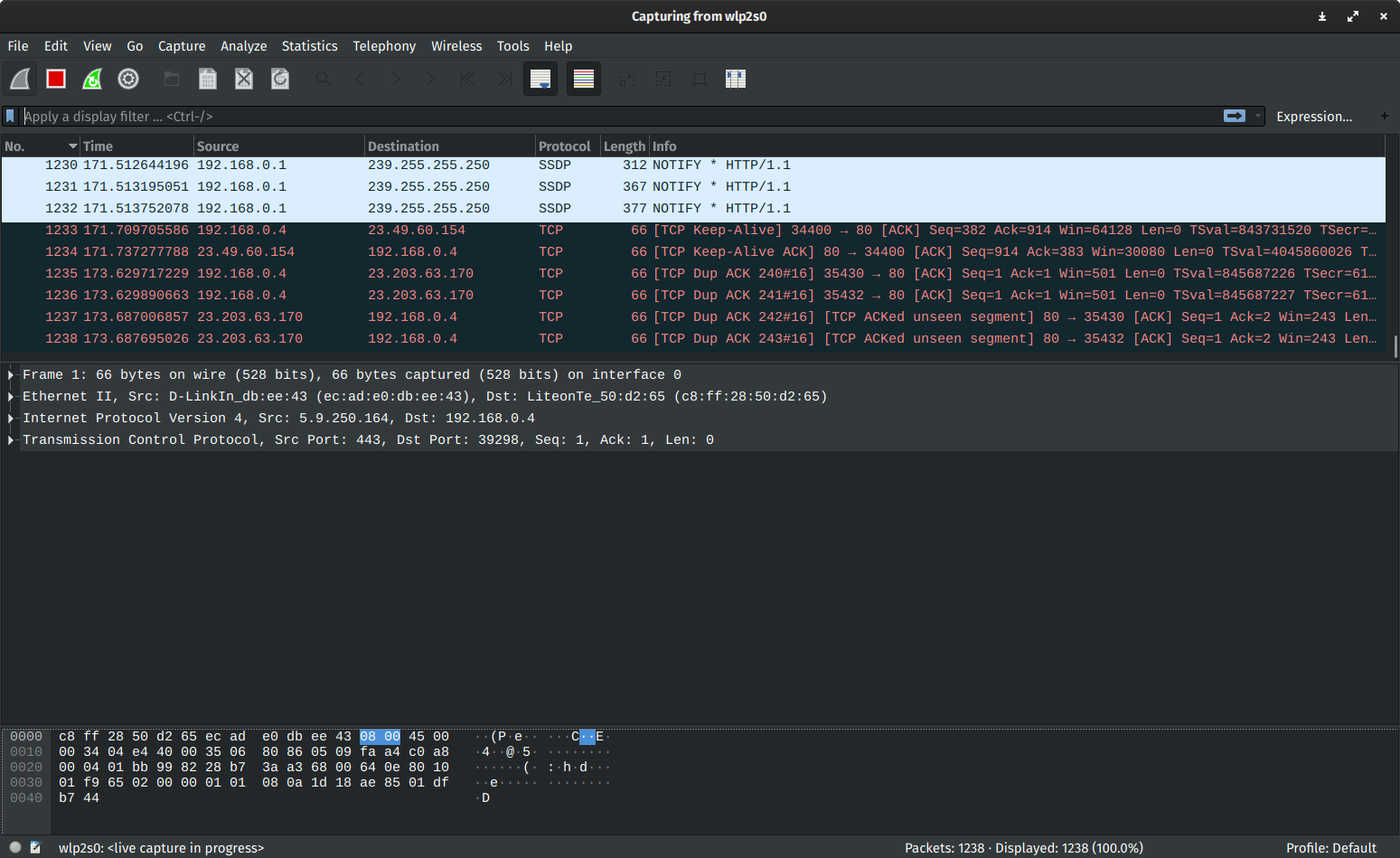
Wireshark is the open-source, world's most famous packet capturer, and analyzer. It runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and many others. It offers a deep inspection of hundreds of protocols and a good GUI.
‣ dSniff:
It is used for network analysis and password sniffing from various
network protocols. It can analyze a variety of protocols (FTP, Telnet, POP,
rLogin, Microsoft SMB, SNMP, IMAP etc) for getting the information.
Microsoft network monitor: As the name suggests it is used for capturing and
analyzing the network. It is used for troubleshooting the network. Get an idea about its work in the window screenshot provided below.

👉Identifying and Preventing Sniffing:
• Avoid connecting to insecure networks. Connecting to any public network will have a risk that the traffic might be sniffed. Attackers choose these public places exploiting the user’s lack of knowledge.
• Using a VPN because it provides strong encryption. Encryption
will ensure that even if the traffic is being sniffed, the attacker will not be
able to make sense of it.
• Network
Scanning and Monitoring: Network admins must monitor the network as well to
ensure device hygiene. Networks must be scanned for any kind of intrusion
attempt.


Comments
Post a Comment